WHAT IS THE REALTIME LABS URINARY TRACT INFECTION PANEL?
For years, the gold standard for UTI diagnosis has been urinalysis and standard urine culture. However, lengthy turnaround times, potential false positive results, and difficulty in reporting speciation and antibiotic susceptibility are among the shortcomings in culture methodology. Thus, newer technologies have now been developed to aid in the diagnosis and treatment of UTIs.
These newer technologies include Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) testing which involves the amplification and detection of targeted DNA. Not only are the urine pathogens (disease-causing organisms) detected by PCR, but the test also screens for antibiotic resistance. Realtime Laboratories, Inc. in Carrollton, Texas, has implemented a UTI PCR test for 17 bacteria, 1 yeast, and 7 genes marking resistance to antibiotics.

Patients are required to fill-out a SURVEY then submit “Medical Release Form” to order the UTI test
Price: $599
Practitioners can order HERE
Become a Provider and start ordering today!
ORGANISMS ON THE RTL UTI PANEL
| Gram Positive Cocci | Gram Negative Bacilli | Yeast |
| Enterococcus faecalis | Acinetobacter baumannii | Candida albicans |
| Enterococcus faecium | Citrobacter freundii | |
| Streptococcus agalactiae | Enterobacter cloacae complex | |
| Staphylococcus xylosus/saprophyticus | Escherichia coli | |
| Klebsiella aerogenes (Enterobacter aerogenes) | ||
| Klebsiella oxytoca | ||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | ||
| Morganella morganii | ||
| Proteus mirabilis | ||
| Proteus vulgaris | ||
| Providencia stuartii | ||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE GENES DETECTED ON RTL UTI PANEL
| Gene(s) | Antibiotics and/or Bacteria Involved |
| mecA | MRSA (Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)/ Beta-lactam resistance |
| blaSHV | Class A Beta-lactam resistant and MRSA/Beta-Lactamase |
| vanB | Vancomycin resistance |
| ermB | Erythromycin resistance |
| sul1 | Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole (Septra/Bactrim) resistance |
| blaKPC | Carbapenem hydrolyzing class A beta-lactamase KPC |
| qnrA | Quinolone resistance |
DISCLOSURE: RTL does not treat or recommend treatments for uncomplicated or complicated UTIs. The information contained here is taken from noted source documents. For further guidance, the reader may contact the Medical Department at RTL concerning any issues regarding UTIs or treatments.
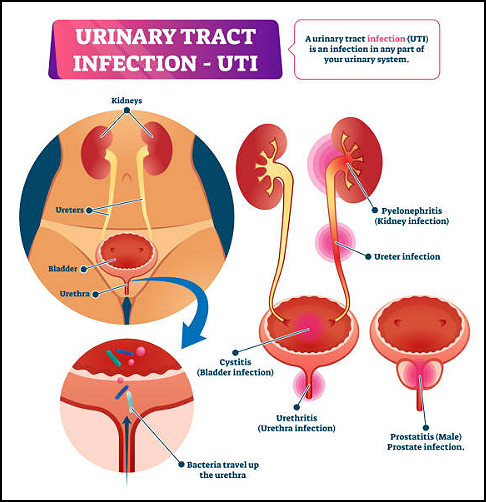
URINARY TRACT INFECTION PANEL
Urinary tract infections (UTI) occur in more than one-half of adult women in the United States. Many will develop at least two infections in a six-month period or may even have three infections within one year. Many national and international bodies have published peer-reviewed documents on uncomplicated and complicated UTIs. The two types of urinary tract infections are shown below.
1. Uncomplicated Lower UTIs or Cystitis
- Female patients without catheters and without any co-morbid conditions.
2. Complicated Lower UTIs or Cystitis
- Men
- Pregnant women
- Women with co-morbid conditions, including but not limited to:
The reader is referred to the Michigan Hospital Medicine Safety Consortium document on Guidelines for Treatment of UTIs. For further information (https://mi-hms.org/sites/default/files/UTI%20Guideline-6.9.21.pdf).
FIVE HEALTHCARE PROVIDER BENEFITS
- Antibiotic Stewardship
*RealTime Labs supports the Core Elements of Antibiotic Stewardship, which includes the effort to improve how antibiotics are prescribed by clinicians and used by patients
* The test targets the infection-causing microbe, either yeast or bacteria.
* The presence of a gene for resistance to antibiotics is determined, which optimizes the physician’s ability to treat infections. This will protect patients from harm caused by unnecessary antibiotic use and thus, improve patient outcomes.
* The reader is referred to the link of CDC showing extensive documents concerning antibiotic stewardship in different patient populations:
i. https://www.cdc.gov/antibiotic-use/core-elements/outpatient.html
ii. https://www.cdc.gov/antibiotic-use/core-elements/nursing-homes.html - Reduced False Negatives
* The test results from RTL will help eliminate false negative results.
* Positive and negative controls are conducted in tandem with each patient’s test. - Reduced Bacterial Resistance with Pathogen Identification
* The international consortium noted here lists treatment modalities to use and/or avoid. https://mi-hms.org/sites/default/files/UTI%20Guideline-6.9.21.pdf
* The treatment modalities recommended in the Michigan Consortium document is as follows:
Uncomplicated Lower Urinary Tract Infection or Cystitis
| Antibiotic | Duration | Considerations |
| Nitrofurantoin | 5 days | Avoid if CrCl < 30 ml/min |
| Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole | 3 days | Increasing E. coli resistance |
| Alternative | ||
| Fosfomycin | 1 dose | Cost ~$60/dose May not be available at some retail pharmacies May consider extending duration to 3-5 doses |
| Oral beta-lactam | 3-7 days | |
Complicated Lower Urinary Tract Infection or Cystitis
| Antibiotic | Duration | Considerations |
| Nitrofurantoin | 7 days | Avoid if CrCl < 30 ml/min |
| Fosfomycin | 48 hrs x 3-5 doses | Cost ~$60/dose May not be available at some retail pharmacies |
| Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole | 3 days | Increasing E. coli resistance |
| Oral beta-lactam, aztreonam in setting of severe penicillin or cephalosporin allergy | 7 days |
Uncomplicated Pyelonephritis
| Antibiotic | Duration |
| Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole | 7-14 days |
| Fluoroquinolones | 5-7 days |
| Beta-lactams | Oral beta-lactam or oral trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole therapy: 7-14 days |
- When incorrect antibiotics are prescribed, pathogens gain strength and become resistant to treatment.
- Antimicrobial resistance has the potential to affect people at any stage of life, as well as the healthcare, veterinary, and agricultural industries.
- This makes it one of the world’s most urgent public health problems.
- Bacteria and yeast do not have to be resistant to every antibiotic or antifungal to be dangerous.
Further Information on Antibiotic Dosage
| Antibiotic | Dose |
| Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (160 mg/800 mg) | 1 DS tablet po BID |
| Nitrofurantoin | 100 mg po BID |
| Fosfomycin | 3 g dose (see tables for complicated and uncomplicated lower UTI) |
| Amoxicillin-clavulanate (Augmentin) | 875 mg po BID Uncomplicated cystitis: 500 mg po BID |
| Cephalexin | 500 mg po BID Uncomplicated cystitis: 500 mg po BID |
| Cefpodoxime | 100-200 mg po BID Uncomplicated cystitis: 100 mg po BID |
| Cefdinir | 300 mg po BID |
| Cefuroxime | 500 mg po BID |
| Ciprofloxacin | 250-750 mg po BID |
- THE 5 Ds of Antibiotic Choice
1. Diagnosis
2. Drug
3. Dose
4. Duration
5. De-escalation (reduction in the spectrum of administered antibiotics through the discontinuation of antibiotics)
* Diagnostic tests should be used wisely to avoid unnecessary antibiotic therapy or therapy that is unnecessarily broad-spectrum, with consideration of healthcare value.
* Rapid diagnostic tests, biomarkers, and decision rules that have acceptable performance characteristics to differentiate bacterial vs. non-bacterial infection should be used to avoid unnecessary antibiotic therapy.
5. Increased Patient Satisfaction with better outcome
* The results from RealTime Labs will help healthcare providers improve patient satisfaction by providing the correct diagnostic tool and results in a timely manner.
* We deliver an overnight kit to patients with simple instructions for specimen collection and return it to the lab by overnight carrier.
* In 8 to 24 hours the results are available for review and an informed decision can be made by the healthcare provider giving personalized treatment for the patient.
* This will improve both patient satisfaction and ultimately result in better outcomes.
FOUR PATIENT BENEFITS OF THE REALTIME LABS URINARY TRACT INFECTION PANEL
- The test is available in all 50 states
- Test kit is sent overnight to your door
- Lab results reviewed upon completion and antibiotic genetic results available to discuss antibiotic selection with the patient’s healthcare provider
- More personalized approach to treating a patient’s condition.